In fact, audio data is becoming an increasingly valuable asset for businesses, researchers, and developers. With the rise of voice assistants, automated transcription services, and machine learning (ML) applications, the need for accurate and efficient audio annotation tools has never been greater. These tools enable precise labeling of sounds, speech, and other audio elements.
In this guide, we’ll discover the top features of audio annotation tools, their use cases, and how to select the suitable audio annotation tool.
What are audio annotation tools?
In general, audio data is gaining importance across industries, from customer service and media to healthcare and AI (artificial intelligence) development. Then, audio annotation tools have become necessary in processing, analyzing, and utilizing large volumes of audio data. These tools provide a structured way to label and categorize audio content, enabling machine learning models to interpret and use the data effectively.
For instance, virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant rely on audio annotation to better comprehend user commands. Automated customer support systems use annotated audio data to distinguish between different speakers, detect sentiment in customer responses, or identify critical keywords. Basically, audio annotation tools are the bridge between raw audio data and machine learning models capable of extracting meaningful insights from it.
Types of audio annotation tools
Different types of annotation may be used depending on the application and the complexity of the audio data. Here, you can discover some of the most commonly utilized types of audio annotation, along with specific tools that support each annotation type.
Transcription
This type of audio annotation involves converting spoken words into written text, which is particularly useful in legal, healthcare, and media industries. In automated systems, transcription allows machines to understand and process voice commands or conversations. Progressive annotation transcriber tools can capture the words spoken and the specific tone and nuances in speech, assisting in improving the accuracy of speech recognition systems.
Sonix is a widely used annotation transcriber tool that offers high-accuracy automatic transcription capabilities. It allows human transcription services to refine speech-to-text conversion accuracy.

Speaker diarization
It is the process of distinguishing between different speakers in an audio recording. This is crucial in meetings, interviews, or customer service calls where multiple people speak. Diarization (a process of automatically partitioning an audio recording into segments) tools label audio sections based on who is speaking, allowing the system to differentiate between speakers. This is especially valuable for AI-driven transcription services or sentiment analysis applications where understanding which speaker said what is critical.
AWS Transcribe provides speaker diarization features, helping separate and label multiple speakers in audio files. This speech analytics technology is helpful for applications like call center analysis or legal transcription where speaker differentiation is essential.
Emotion labeling
It focuses on identifying and tagging emotional states expressed in speech. This is highly beneficial in customer service, therapy applications, and social media monitoring, where sentiment analysis is key. By detecting emotions such as anger, happiness, or frustration, AI voice analytics systems can better understand the context of a conversation and respond accordingly. For example, a system that detects a frustrated customer in real time can escalate the issue to a human operator or offer more appropriate responses.
audEERING’s openSMILE is a powerful annotation platform that analyzes emotional content in speech. It detects various emotional states and is widely used in sentiment analysis, customer service, and healthcare applications.

Phoneme annotation
It deals with marking the individual units of sound in speech—known as phonemes. This annotation type is critical for training speech recognition systems, language learning apps, and AI-powered voice assistants. Phoneme-level annotation enables machines to understand words and the specific sounds that make up those words, thereby improving speech-to-text accuracy and linguistic comprehension.
ELAN is a commonly used online annotation tool. This tool allows for detailed sound analysis and annotation at the phoneme level, improving speech recognition models’ ability to process different languages and accents.
Acoustic event detection (AED)
It goes beyond spoken words to recognize and categorize other sounds in an audio recording. This could include background noises like traffic, alarms, or animal sounds. AED is particularly valuable in security, surveillance, and environmental monitoring applications. For example, smart home systems equipped with AED can detect glass breaking, smoke alarms, or other emergency sounds and immediately alert the homeowner or authorities.
Audacity is a popular speech analytics technology for acoustic event detection. It is designed to analyze and classify environmental sounds in audio data, making it ideal for smart home applications and security systems.
Semantic segmentation
It involves dividing an audio file into meaningful segments based on its content. This technique is often used in multimedia production, podcasting, and music analysis, where different recording sections may need to be tagged for specific purposes. For example, a podcast might be segmented into intro, discussion, guest interview, and conclusion segments, with each part tagged for easier editing or navigation.
Descript is an excellent tool for segmenting audio into relevant parts, especially for podcasts, interviews, and music tracks. This audio annotation tool allows users to easily label and edit specific sections of audio files for different purposes.
Key features of powerful audio annotation tools
The effectiveness of these audio annotation tools largely depends on their features, which enhance usability, efficiency, and collaboration. Let’s check them in more detail.
User-friendly interface
A user-friendly interface is the basis of any effective audio annotation tool. An intuitive and easy-to-navigate platform is essential given the complexity of annotating audio data—whether it involves transcription, speaker diarization, or emotion labeling. The best audio annotation tools offer interfaces designed with simplicity and accessibility, catering to technical and non-technical users.
For example, clear layout designs, easily accessible menus, and drag-and-drop features simplify the annotation process. Tools with customizable views allow users to arrange their workspace to suit their preferences, whether to highlight specific audio sections or annotate multiple files simultaneously. A user-friendly interface reduces the learning curve, enabling faster onboarding and more efficient data annotation workflows.

Reliable Data Services Delivered By Experts
We help you scale faster by doing the data work right - the first time

Automation capabilities
These capabilities are another key feature of modern audio annotation tools. The rise of AI and machine learning has introduced powerful algorithms that can automate various aspects of the annotation process, reducing the amount of manual work required and increasing the speed of project completion.
Automation can assist with repetitive tasks such as transcribing long audio files, identifying speakers, and tagging emotional states. For example, many tools now offer AI powered speech analytics platforms, which can convert spoken words into text with high accuracy. Similarly, automated speaker diarization can differentiate between multiple voices, automatically labeling audio sections by the speaker without human intervention.
Emotion detection is another area where automation shines. Advanced tools can analyze vocal tones, pitch changes, and other acoustic features to determine emotional cues in conversations.

Customizable annotation schemas
Audio data is diverse, and various projects require different types of annotations. Customizable annotation schemas allow users to tailor their annotation workflows to their project’s specific needs, making this feature one of the most essential advanced audio annotation tools.
For instance, some projects may require basic transcription, while others might need more complex labeling, such as speaker identification, emotion tagging, or acoustic event detection. Customizable schemas enable users to define their categories, labels, and metadata fields to meet the unique requirements of their use case.
These schemas also allow for seamless integration with other tools and systems, ensuring compatibility with AI/ML models during the data annotation. This adaptability boosts both productivity and precision, making it easier for companies to train and fine-tune their machine-learning models with high-quality, tailored data. To scale these annotation processes effectively, explore our guide on boosting annotation throughput at scale.
Collaborative features
Collaboration is critical in projects involving large teams or when working on extensive datasets. Advanced audio annotation tools provide collaborative features that enhance teamwork, communication, and overall productivity. These tools are designed to support multiple users working on the same project simultaneously, regardless of their location.
Collaborative features typically include real-time access to shared audio files, enabling team members to annotate audio data concurrently. Tools with version control ensure that all changes are tracked and past versions of the annotations can be retrieved if needed. This prevents data loss and ensures consistency throughout the annotation process.
Many audio annotation programs also offer integrated communication platforms, such as chat or comment sections, where team members can provide feedback, ask questions, or clarify instructions. These features are particularly useful in environments with paramount quality control and accuracy. For instance, an annotation supervisor can leave comments on specific segments, asking team members to correct or refine their annotations.
Moreover, assigning different roles within the audio annotation tool can streamline project management. For example, administrators can manage workflows, assign tasks, and oversee quality assurance, while annotators focus solely on tagging and labeling the data. This division of labor ensures smooth operations, even on large-scale annotation projects.
Choosing the right audio annotation tool
With a wide range of options available, choosing the proper audio labelling tool requires careful consideration of several vital factors. Below are some crucial tips to guide you through the selection process.

1. Define your annotation needs
Different data annotation tools are designed for various audio data and tasks, so it’s crucial to identify what kind of annotation you require. For instance, some projects may involve basic transcription, while others may require more advanced features like speaker diarization, emotion recognition, or phoneme annotation.
If your main goal is to convert speech to text, choose an annotation platform with robust automatic transcription capabilities. For projects distinguishing between multiple speakers, such as meeting transcriptions or interviews, prioritize tools offering robust speaker diarization features. If your project requires emotion detection in customer service calls or therapy sessions, look for tools to analyze vocal tone, pitch, and other acoustic elements.
2. Evaluate ease of use
A user-friendly interface helps reduce the learning curve and ensures that both technical and non-technical team members can work efficiently. Consider the following aspects of usability:
- Intuitive interface: Look for an audio labelling tool with a clean, intuitive design that simplifies the annotation process. Features like drag-and-drop functionality, waveform visualization, and easy navigation between audio segments can significantly improve the user experience.
- Accessibility: If your team includes remote workers or collaborators from different locations, choosing a tool that supports cloud-based access is important. This allows users to work from anywhere without complex software installations or hardware requirements.
- Training and support: Some tools have built-in tutorials, documentation, and customer support. Access to comprehensive resources can help users get up to speed with the tool, reducing the time spent troubleshooting issues.
3. Check for customizable annotation schemas
Projects often have unique requirements that may not align with predefined annotation categories in many tools. Therefore, choosing an audio annotation tool that offers customizable annotation schemas is essential. This lets you define your categories, labels, and metadata fields.
Some projects may require specific labels for phonemes, acoustic events, or other sound types. The ability to create and customize these labels ensures that your data is annotated according to the exact needs of your machine-learning model.
If your organization works on multiple projects with varying objectives, customizable schemas allow you to adapt the tool for each use case, making it versatile and suitable for various tasks.
Customizable workflows allow you to set up different stages of annotation, quality control, and feedback, ensuring that the tool can handle even the most complex audio data annotation.
4. Look for collaborative features
Many audio annotation projects require team collaboration, especially in large-scale or complex projects involving multiple annotators. Moreover, it’s essential to choose best annotation tools that support collaboration:
- Real-time collaboration: Audio annotation tools that enable multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously can significantly improve productivity. Real-time access to shared audio files and annotations ensures team members always work on the most up-to-date data.
- Version control: Version control features allow teams to track changes, review past annotations, and revert to earlier versions if necessary. This is particularly useful for maintaining accuracy and consistency in annotations.
- Role-based access: Some tools offer role-based access controls, allowing administrators to assign specific roles to team members (e.g., annotators, reviewers, and project managers). This feature helps streamline project management and ensures each team member can access the appropriate features.
Challenges in using audio annotation tools
While audio annotation tools offer numerous advantages, users often face various challenges that can hinder the annotation process. Comprehending these common issues can help organizations prepare and implement effective mitigation strategies.

Accuracy and quality of annotations
Audio labelling tools, while helpful, are not always perfect. Factors such as background noise, overlapping speech, accents, and technical jargon can lead to errors in transcription and mislabeling.
Audio files often contain extraneous sounds, confusing automated tools and leading to inaccuracies. In environments with poor sound quality or multiple speakers, distinguishing relevant audio segments becomes increasingly difficult.
Variations in speech, including accents and dialects, can affect the performance of automated transcription tools. These tools may struggle to interpret or transcribe words accurately, resulting in errors that require manual correction.
Scalability issues
Managing large datasets often requires coordination among multiple annotators and ensuring consistency across their work. This can lead to discrepancies in how audio segments are labeled and interpreted.
When multiple annotators work on the same project, variations in interpretation and labeling can arise. This inconsistency can undermine the dataset’s quality, making it less reliable for training machine learning models.
Scaling annotation efforts may require training new annotators, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Ensuring all team members are aligned on audio data annotation guidelines is crucial for maintaining consistency.
Complexity of annotation tasks
Depending on the project, annotators may need to engage in various forms of labeling, such as speaker diarization, emotion detection, or acoustic event identification. This complexity can lead to confusion and errors during the audio data annotation process.
Different projects may require different types of annotations, and annotators must be well-versed in various methods and techniques. For instance, emotion labeling requires a nuanced understanding of vocal tones and contexts, which can be subjective.
Complex tasks may demand significant time and effort from annotators, leading to longer project turnaround times. Balancing thoroughness with efficiency is essential for meeting project deadlines.
Tool limitations
While audio annotation tools can be powerful, they often have limitations that hinder their effectiveness. Understanding these limitations is essential when choosing a tool for a specific project.
Some tools may not allow for customizable annotation schemas, making it difficult to adapt them to specific project requirements. This can limit the tool’s versatility and require additional effort to align with project needs.
While automation can streamline the annotation process, not all tools offer the same level of automation. Tools with limited automation capabilities may require extensive manual work, reducing efficiency and increasing the likelihood of human error.
Data privacy and security concerns
Many audio files contain personal or confidential data, especially in healthcare, finance, and customer service.
Organizations must ensure that their audio data annotation processes comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which govern data privacy and security. Failing to comply can result in severe penalties and reputational damage.
Protecting annotated data from unauthorized access is crucial. Organizations need to implement robust security measures, including encryption and access controls, to safeguard audio files and annotations.
Audio annotation services at Tinkogroup
Our extensive experience in audio annotation services has equipped us with the knowledge and expertise to deliver high-quality annotations that meet the diverse needs of our clients across various industries.
We have completed numerous healthcare, finance, and entertainment client projects. Each project has helped us refine our processes, improve our annotation quality, and adapt to the specific requirements of different industries. Our commitment to delivering high-quality annotations has earned us a reputation as a reliable business partner leveraging audio data.
At Tinkogroup, we employ advanced annotation tools and human expertise to ensure that our annotations are accurate and contextually relevant. We utilize advanced technology, including automated transcription software, emotion recognition algorithms, and speaker diarization tools. However, we firmly believe in the irreplaceable value of human oversight.
Our annotation process involves several essential steps:
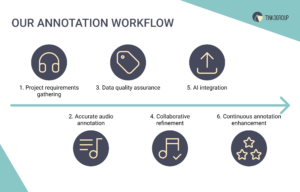
- Project requirements gathering: We receive a ready dataset and efficiently process it to create a customized annotation plan.
- Accurate audio annotation: Our team accurately labels audio files using specialized audio annotation tools and techniques.
- Data quality assurance: We implement a multi-layered quality assurance process to guarantee high-quality annotations.
- Collaborative refinement: Our team works closely with clients, continuously incorporating feedback to improve the annotation process.
- AI integration: We ensure seamless integration of annotated data with your AI systems for optimized machine learning results.
- Continuous annotation enhancement: Our experts offer ongoing support to refine and optimize your annotation data for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
The audio annotation tools streamline the process of organizing and labeling audio data and improve the accuracy and efficiency of applications. Businesses and developers can discover the full potential of their audio data by choosing the right audio annotation tool.
At Tinkogroup, we provide robust data annotation services that ensure accuracy and efficiency for all your AI and machine learning needs. Contact us to discover how we can support your project with reliable annotations and accelerate your path to success!
How do I annotate audio files?
First, collect the audio recordings you want to work with. Next, choose an appropriate audio annotation tool that suits your project's needs. After setting up the tool, you can start annotating by listening to the audio and applying labels or transcriptions as required.
What is an audio annotator?
An audio annotator is a person or software that labels or categorizes audio data for various purposes, typically to prepare the data for ML and AI applications. Audio annotators may transcribe spoken words, identify speakers, label emotions conveyed in the speech, or categorize specific sounds.
What is an annotation tool in AI?
An annotation tool in AI is software designed to facilitate labeling and categorizing data, including audio, text, images, and video. These tools provide features that help users annotate data efficiently, such as customizable schemas, automation capabilities, and collaborative functionalities.





